Developing microwave-assisted ionic liquid microextraction for the detection and tracking of hydrophobic pesticides in complex environmental matrices
- 文件格式 :
Developing microwave-assisted ionic liquid microextraction for the detection and tracking of hydrophobic pesticides in complex environmental matrices
Jing Wang, Jian Xiong, Gary A. Baker, Renee D. JiJib and Sheila N. Baker
Abstract
In the present study, we have developed a novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) based on microwave-assisted DLLME (MADLLME) using
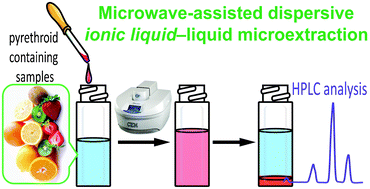
標簽: 離子液體 TFSI-ILs LiTFSI 農藥殘留
